 The Structure of Intermediaries in Saharanpur
The Structure of Intermediaries in Saharanpur
Abstract
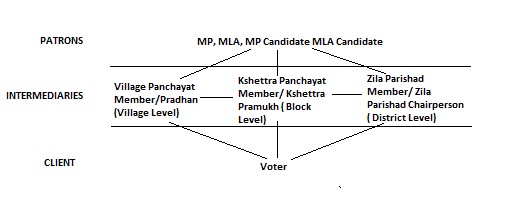
In this article, we examine the role of intermediaries in sustaining political clientelism in rural Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh. Drawing from fieldwork and electoral data, we show that clientelism in Saharanpur is based around providing three specific guarantees to the voter—security from or by the police, facilitation in the tehsil and mediation in cases that would otherwise go to court—which we collectively refer to as guardianship. We explain how guardianship, more than most other forms of clientelistic exchange, requires intermediaries. In the case of Saharanpur, these intermediaries are usually individuals occupying formal positions of power within various circles of Panchayati Raj Institutions. Finally, we argue that it is the concentric nature of constituencies provided by the decentralized political structure which is ultimately responsible for the sustenance of intermediary networks as well as the perpetuation of clientelism in rural Saharanpur.